Everything you need to know about "Leveraged Forex Trading" (Part 2)
Explore the dynamics of Forex leveraged trading, including its benefits, risks, and key strategies for effective risk management.


Table of Contents
The article discusses the principles of leveraged trading in Forex, highlighting both its advantages and disadvantages. Leveraged trading allows traders to control large positions with a relatively small amount of invested capital, potentially increasing profits. However, it also amplifies risks and can lead to substantial losses, especially if traders disregard risk management principles. The article further explains the concept of leverage ratio and how it is used in trading, providing formulas and examples for better understanding. It concludes with practical examples demonstrating the impact of different leverage levels on trading outcomes.
Understanding Forex Leverage: Advantages, Risks, and Strategic Use
Maximize your trading potential with informed leverage strategies—Learn more about Forex leveraged trading today!
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Advantages of Leveraged Trading | Increases trading volume, amplifies potential profits, no interest on borrowed funds. |
| Disadvantages of Leveraged Trading | Higher risk, potential for large losses, psychological traps, and margin calls. |
| Leverage Ratio Explanation | Ratio of capital to buy margin, important for understanding trade size and risk. |
| Calculating Leverage | Depends on the asset; formula involves total assets and margin used. |
| Practical Examples | Demonstrates effects of different leverage levels on trading outcomes. |
Advantages of Leveraged Trading
The advantages of Forex leveraged trading are:
- You are able to trade with much larger volumes than your own funds.
- Leverage is an interest-free loan. In order to increase your deposit and trade larger volumes, you can take out a loan from a bank, but you will have to pay interest. Forex brokers offer you leverage without charging interest.
- You can use leverage to increase your earnings. If you use leverage to increase your trading volume by 10 times, your profit will also increase by 10 times (I wrote about this before).
- In the case of the same assets and the same trading volume, the unleveraged deposit will be stopped earlier than the leveraged deposit.
Go to LiteFinance Official Website
Disadvantages of Leveraged Trading
The disadvantages of using Forex leveraged trading include:
- The total volume of open positions increases and the associated risk is higher. As the open interest increases, the pip value also increases. Therefore, your potential loss also increases. High leverage means potentially high profits and high losses at the same time.
- Margin call/stop loss. This problem stems from the previous point. If you trade EUR/USD with a volume of 1 lot, a pip costs $10.
- If the open interest is 0.01 lots, one pip costs 10 cents. In the first case, the deposit will be stopped faster.
- Psychological trap. When you have free funds with the help of leverage to meet margin requirements. If you want to win back your losses, it will encourage you to increase your position size, causing you to increase your losing trades. It can also lead to unreasonable confidence in your potential profits.
All the drawbacks of leverage mentioned above are only downsides when traders forget the rules of risk management and increase their positions at the behest of their emotions. If you use your broker’s leverage (even high leverage) without increasing your open interest, there is no risk.
Leveraged products (how to calculate leverage for different trading assets)
So, now I believe you understand the general meaning of margin and leverage. Let me briefly summarize:
- Financial leverage is an interest-free loan from a broker that enables you to buy more assets or lower your margin, saving money that the broker keeps as collateral.
- Margin is money (real money on your account) that a trader keeps as collateral by a broker when making a trade. It is calculated according to the “Open Interest/Leverage” formula.
- Stop loss in Forex is the level at which a broker automatically closes all active positions of a trader, and it is a percentage determined by trading conditions. In turn, this level is calculated using the formula “Total Assets (or Total Funds) / Used Assets (Margin, Collateral) * 100”.
The above concepts are needed to develop a risk management system and to calculate acceptable risk levels. The above formula only applies to currency CFDs traded in Forex. For other trading instruments, the calculation formula is different. Likewise, the concept of leverage in stock trading is different from the definition of leverage in forex, which is borrowed funds provided by a broker.
Go to LiteFinance Official Website
Leverage ratio: what is it?
In economics, the financial leverage ratio shows the actual ratio of owned funds to borrowed funds in a business. This indicator allows you to assess the stability of the company and its level of profitability. In Forex, the term has a slightly different meaning. Forex leverage is the ratio of capital to buy margin.
Leverage Ratio Formula
The coefficient formula is simple: 1/leverage. For example, a leverage ratio of 1:2 leverage is 1/2 = 0.5. For a leverage of 1:100, the leverage ratio is 1/100 = 0.01.
Example of calculating margin requirements and account balances:
You have a deposit of $3000. You want to buy 1 lot of EUR (100 000 EUR) at 1.2 USD. The broker offers a maximum leverage of 1:50 for this currency pair.
The leverage ratio is 1/50 = 0.02.
Margin = 100,000 * 1.2 * 0.02 = $2400 – this is the amount the broker keeps when offering 1:50 leverage.
Free funds (available for operations) are 3000-2400 = $600.
By using 1:50 leverage, you can manage 600 * 50 = $30,000 of funds. With this money, you can buy 30,000 / 1.2 = 25,000 EUR. In other words, buying EUR 25,000 with a leverage of 1:50 has a margin of $600.
Using $3000 and a leverage of 1:50, you can buy a total of EUR 125,000. The simple calculation formula is as follows: Purchase amount = 3000 * 50 / 1.2 = 125,000 EUR.
Before calculating the best forex leverage, I recommend you to use a forex calculator, which can provide a lot of other useful information in addition to calculating margin values. It looks like this:
Go to LiteFinance Official Website
Forex Leverage Calculator
Not sure how to calculate leverage in the Forex market? Use a leverage calculator. It’s simple and easy to use:
- Choose the currency pair or any other asset you want to trade.
- Choose the leverage you want to use.
- Select the lot size you want to open.
That’s it. The calculator will show you the amount of margin required to trade with the leverage of your choice and, in addition to that, the actual cost of the trade (if not using borrowed funds).
For example, to open a EURUSD buy position with a volume of 0.01 lots and a leverage of 1:100, the margin would be $11.32. In other words, to buy 1000 EUR, you need $1132, but the leverage on that amount is 1/100, so $11.32 would be enough for you to trade.
Example of leverage ratio in trading
To explain to you the difference between low-leverage and high-leverage trading, I will again use the EURUSD currency pair as an example. I will use 1:10 leverage and 1:1000 forex leverage.
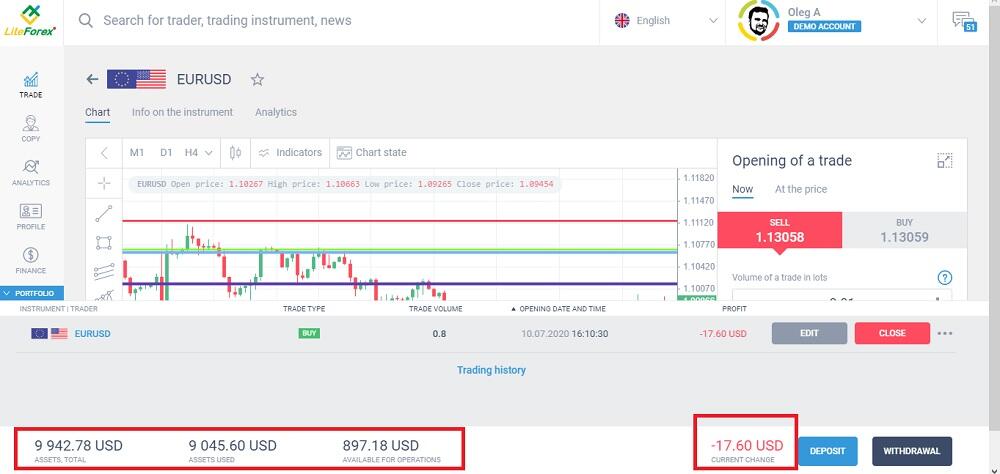
Deposit less than $10,000. This means that with 1:10 leverage, I can trade 0.8 lots (collateral = 80,000 / 10 * 1.13 = 9040).
Funds available for operations are just under $1,000. Please note the current changes. Within minutes of trading in the market, floating losses reached double digits.
Now, I changed the leverage to 1:1000. Using the same deposit, I can open a position with 80 (!) lots (collateral = 8,000,000 / 1,000 * 1.13 = 9040). That is, with a deposit of less than $10,000, I can buy 8 million euros.
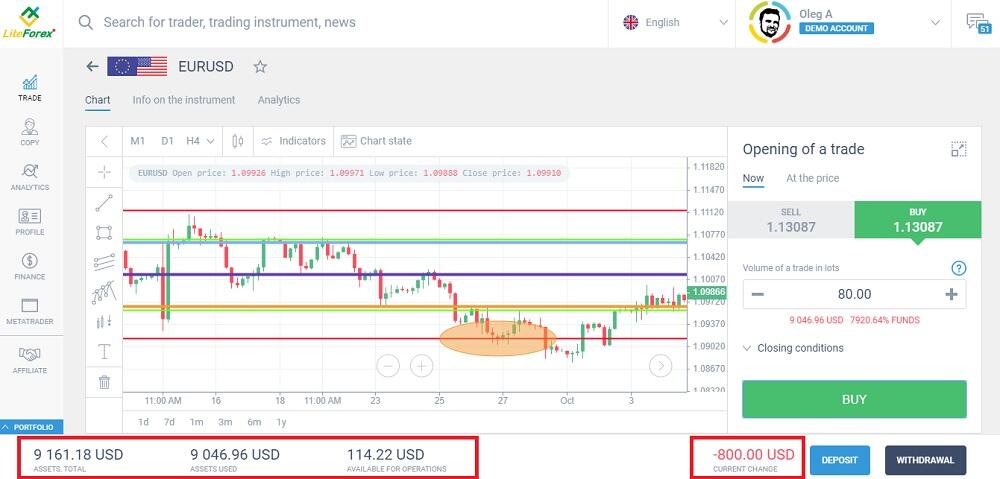
The current loss is now in the triple digits, although the amount of assets used is the same. However, the amount of assets available for operations is much less because the leverage is higher and the pip value is much higher. I waited a few minutes and then exited the transaction.
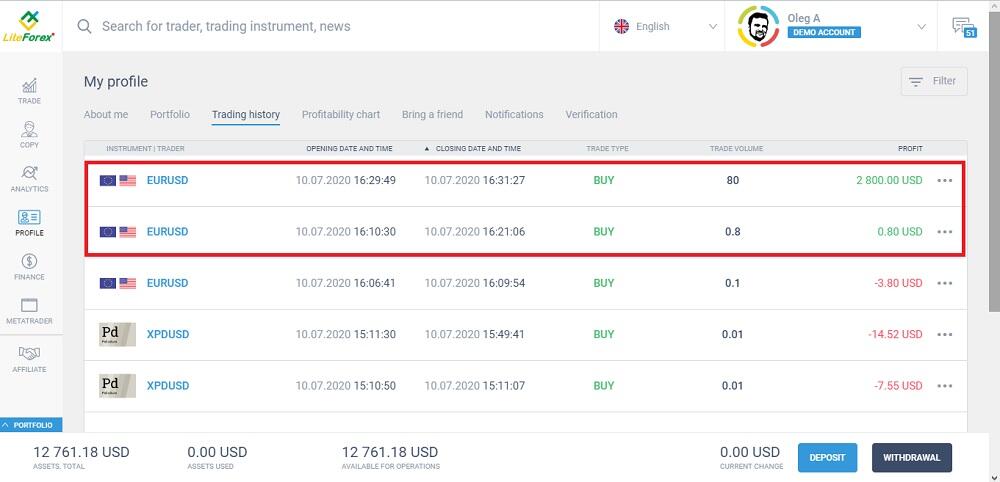
The chart above shows the results of two trades using 1:10 and 1:1000 leverage. These positions were only held for a few minutes. The deposit is the same, and so is the collateral. In the first case, the profit is $0.8, and in the second case, the profit is $2800.
At first, the advantages of high leverage seem obvious. But keep in mind that as the trade size increases, so does the pip value.
With lower leverage, available funds are close to $900. With high leverage, available funds are less than $150.
If the price falls just a few pips, the trade will be stopped out. For a leverage of 1:10, the price range is longer and the trade is safer.
In conclusion, the higher the leverage used to increase trading volume, the greater the potential profit. However, there is also a greater risk that the trade will be stopped and lose the deposit.
I will explain further how to choose a leverage ratio and how to use leverage in forex trading.
Go to LiteFinance Official Website
Example of using maximum leverage
Example 1. Suppose you seize a good moment at the beginning of a EUR/USD uptrend. You have a deposit of $120 and the current exchange rate is 1.2. You have leverage of 1:1000, so with $120,000, you can buy EUR 100,000 (ie 1 lot). The EUR/USD pip value for 1 lot volume is $10.
This means that if the price falls by only 12 pips, you will lose your entire deposit (assuming a stop loss level of 0). You open the volatility calculator and see that EUR/USD has average volatility of about 80 pips.
In conclusion, if you use 1:1000 leverage, you will most likely lose your entire deposit. In the event of a trend reversal or local correction, the price will definitely move 12 pips.
Example 2. Suppose you have a deposit of $1200 and you can make a trade with a volume of 0.01 lots. Without leverage (1:1 leverage), the margin would be $1200. But you want to hedge your risk and make another trade for a negatively correlated asset.
You use 1:1000 leverage and your margin is $1.2. You are free to control the remaining $1198.8 and trade another asset with the same volume of 0.01 lots.
In conclusion, by using the maximum forex leverage, you are not taking any risk, as the total volume of trades made will be 0.02 lots (pips will be calculated in cents, and you will not lose your deposit in the event of an opposite price movement). On the other hand, your profit won’t be much.
Example 3. Each of the 2 orders has an open position of $5000. The first position is opened with leverage of 1:1 with a margin of $5000. The second position is opened with a leverage of 1:100 and a margin of $50. The formula for stop loss level is asset value/margin*100%. Stop Loss is the level at which a position is forced to close out (for example, a Stop Loss level of 20% means that once the 20% level is reached, all positions will be automatically closed).
Since the position size (numerator) is the same in both cases, the only difference is in the denominator. Therefore, the stop loss level value in the first case will be greater than that in the second case.
In conclusion, with the same position size, if there is a loss, the leveraged position will be stopped later than the unleveraged position. In other words, using leverage reduces the risk of stop loss.
FAQs
- What is leveraged trading?
- Leveraged trading allows traders to control larger positions than their own capital would normally permit, by using funds borrowed from a broker.
- What are the main advantages of leveraged trading?
- The main advantages include the ability to trade larger volumes and potentially increase profits without a proportional increase in investment.
- What are the risks of leveraged trading?
- Risks include increased potential losses, higher volatility exposure, and the psychological effect of managing larger trades.
- How is the leverage ratio calculated?
- The leverage ratio is calculated as the inverse of leverage; for example, a leverage of 1:100 translates to a leverage ratio of 0.01.
- What is a margin call?
- A margin call occurs when the trader’s equity falls below a required level, forcing them to add funds or close positions to cover the possible losses.
- How does leverage affect trading losses?
- Higher leverage increases the value of each pip move, which can amplify losses if the market moves against the trader’s position.
- Can leverage be different for different assets?
- Yes, leverage can vary based on the asset being traded, as different assets have different volatility and risk profiles.
- What should traders consider before using leverage?
- Traders should consider their risk tolerance, trading strategy, and the specific terms of leverage offered by their broker.
- What is a practical example of using leverage?
- An example is trading EUR/USD with a leverage of 1:100, allowing the trader to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital.
- How can traders minimize risks when using leverage?
- Traders can minimize risks by employing strict risk management strategies, setting stop-loss orders, and not overextending their market exposure.
Latest Features
- Close






